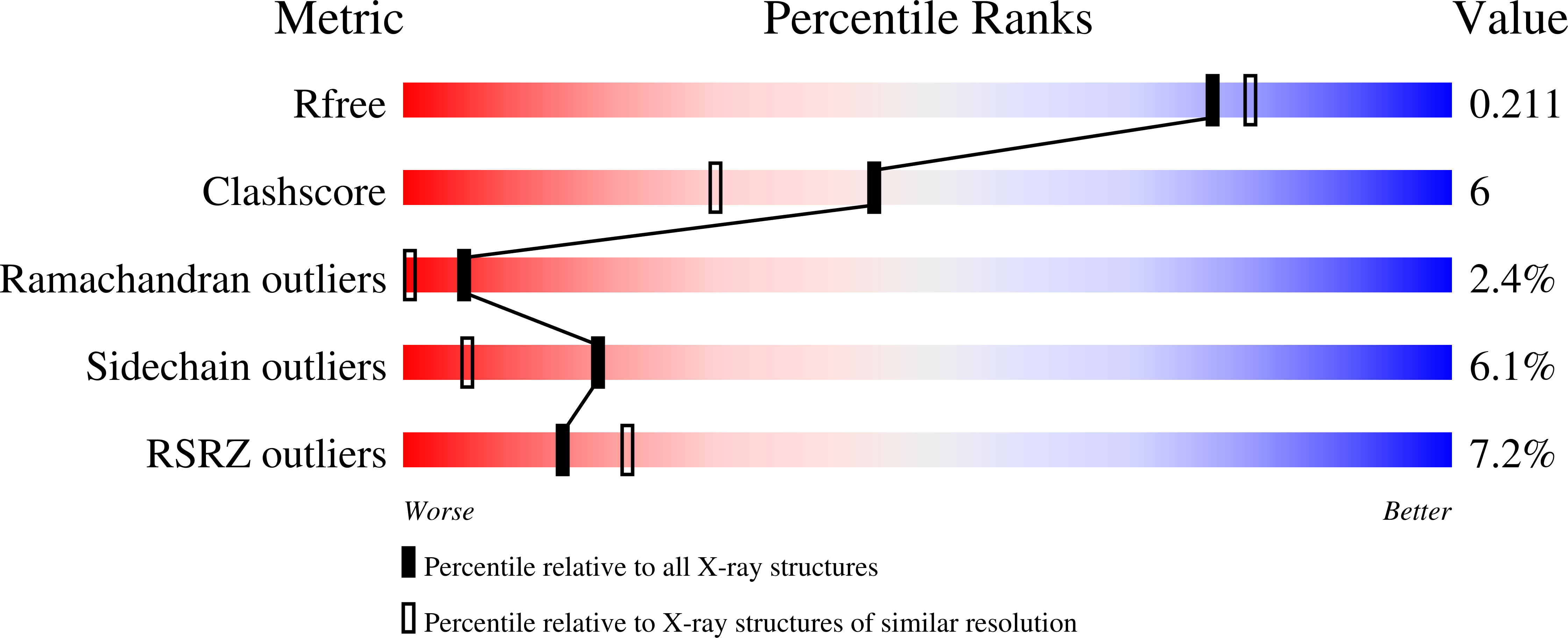
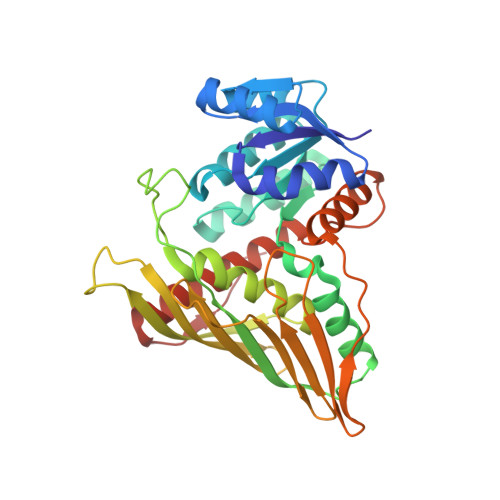
The structure of substrate-free 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose reductase from Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 reveals an open enzyme conformation.
Schu, M., Faust, A., Stosik, B., Kohring, G.W., Giffhorn, F., Scheidig, A.J.(2013) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 69: 844-849
- PubMed: 23908025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309113019490
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4KOA - PubMed Abstract:
1,5-Anhydro-D-fructose (1,5-AF) is an interesting building block for enantioselective and stereoselective organic synthesis. Enzymes acting on this compound are potential targets for structure-based protein/enzyme design to extend the repertoire of catalytic modifications of this and related building blocks. Recombinant 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose reductase (AFR) from Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 was produced in Escherichia coli, purified using a fused 6×His affinity tag and crystallized in complex with the cofactor NADP(H) using the hanging-drop technique. Its structure was determined to 1.93 Å resolution using molecular replacement. The structure displays an empty substrate-binding site and can be interpreted as an open conformation reflecting the enzyme state shortly after the release of product, presumably with bound oxidized cofactor NADP⁺. Docking simulations indicated that amino-acid residues Lys94, His151, Trp162, Arg163, Asp176 and His180 are involved in substrate binding, catalysis or product release. The side chain of Lys94 seems to have the ability to function as a molecular switch. The crystal structure helps to characterize the interface relevant for dimer formation as observed in solution. The crystal structure is compared with the structure of the homologue from S. morelense, which was solved in a closed conformation and for which dimer formation in solution could not be verified but seems to be likely based on the presented studies of S. meliloti AFR.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Zoology - Structural Biology, Christian-Albrechts University Kiel, Am Botanischen Garten 1-9, 24118 Kiel, Germany.